လျှပ်စစ်မော်တာသည် လျှပ်စစ်စွမ်းအင်ကို လျှပ်စစ်သံလိုက်လုပ်ဆောင်ချက်ဖြင့် စက်စွမ်းအင်အဖြစ်သို့ ပြောင်းလဲပေးသည့် ကိရိယာတစ်ခုဖြစ်သည်။
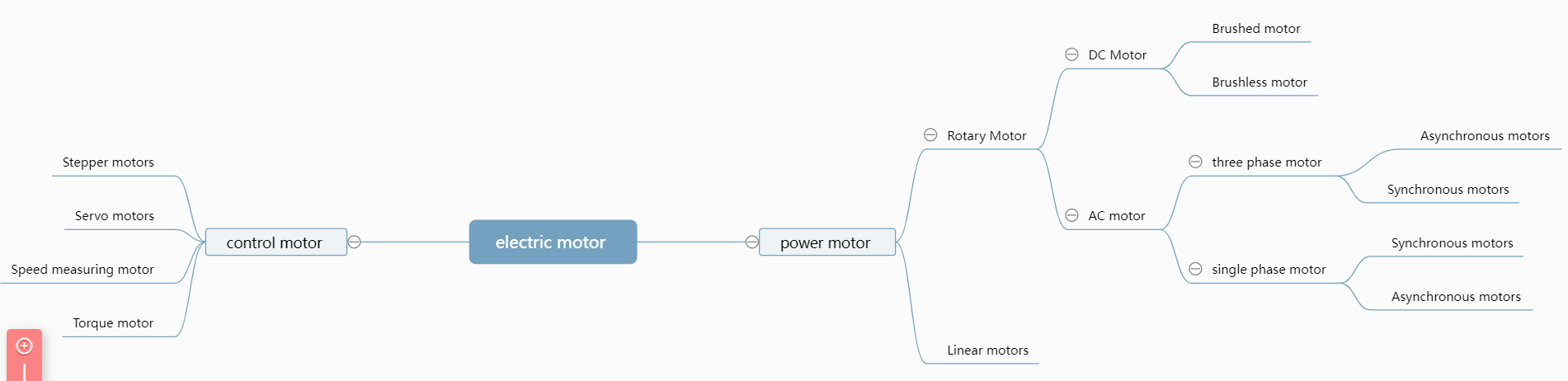
လျှပ်စစ်စွမ်းအင်ပုံစံဖြင့်၊ မော်တာများကို AC မော်တာနှင့် DC မော်တာဟူ၍ နှစ်မျိုးခွဲခြားနိုင်သည်။
၎င်းတို့တွင် AC မော်တာများကို single-phase AC motors နှင့် three-phase AC motor ဟူ၍ ခွဲခြားနိုင်သည်။ လည်ပတ်မှုနှုန်းကွာခြားမှုအရ ၎င်းကို အမျိုးအစားခွဲခြင်းနိယာမအရ မော်တာကို synchronous motors နှင့် asynchronous motors ဟူ၍ ခွဲခြားနိုင်သည်။
synchronous motors များကို မတူညီသော သံလိုက်စက်ကွင်းများအလိုက် အမြဲတမ်း သံလိုက်ထပ်တူသော မော်တာများ၊ hysteresis synchronous motors နှင့် reluctance synchronous motors များအဖြစ် ခွဲခြားနိုင်ပါသည်။
အခြားတစ်ဖက်တွင်၊ Asynchronous မော်တာများသည် induction ပုံစံတွင်သာမက AC ကွန်မြူတာတာပုံစံတွင်ပါ ရရှိနိုင်သည်။
Induction ပုံစံကို သုံးဆင့် အဟန့်အတားဖြစ်စေသော မော်တာများနှင့် အရိပ်-ဝင်ရိုးစွန်း အတိုင်းအဆမဲ့ မော်တာများ ဟူ၍ ခွဲခြားနိုင်သည်။ ထို့အပြင် အကာအကွယ်အမျိုးအစားအလိုက် မော်တာအား အပိတ်၊ အဖွင့်၊ ရေစိုခံ၊ ရေငုပ်သွင်းနိုင်သော၊ ရေစိုခံ၊ နှင့် ပေါက်ကွဲဒဏ်ခံနိုင်သော မော်တာဟူ၍လည်း ခွဲခြားနိုင်သည်။
Electric Motor သည် လျှပ်စစ်သံလိုက် လျှပ်စီးကြောင်း ဥပဒေနှင့်အညီ လျှပ်စစ်စွမ်းအင်သို့ ကူးပြောင်းခြင်း သို့မဟုတ် ကူးပြောင်းခြင်းအား သိရှိနားလည်စေရန် လျှပ်စစ်သံလိုက်နှင့် ထိန်းချုပ်မှုစနစ်၏ အရေးကြီးသော အစိတ်အပိုင်းတစ်ခုဖြစ်ပြီး အဓိကအခန်းကဏ္ဍမှာ လျှပ်စစ်ဓာတ်အား အရင်းအမြစ်အဖြစ် မောင်းနှင်အားအား ထုတ်ပေးရန်ဖြစ်သည်။ စက်ပစ္စည်း သို့မဟုတ် စက်ပစ္စည်းအမျိုးမျိုးနှင့် လျှပ်စစ်စွမ်းအင်ကို စက်စွမ်းအင်အဖြစ်သို့ ပြောင်းလဲပါ။
ခေတ်မီသိပ္ပံနှင့်နည်းပညာများ ဖွံ့ဖြိုးတိုးတက်လာသည်နှင့်အမျှ၊ လက်တွေ့အသုံးချမှုများတွင် မော်တာများ၏အာရုံကို ယခင်က ရိုးရှင်းသောဂီယာမှ ရှုပ်ထွေးသောထိန်းချုပ်မှုဆီသို့ ပြောင်းလဲလာခဲ့ပြီး အထူးသဖြင့် မော်တာအမြန်နှုန်း၊ အနေအထားနှင့် torque တို့ကို တိကျစွာထိန်းချုပ်ရန်အတွက်ဖြစ်သည်။
သို့သော်လည်း မော်တာများသည် မတူညီသော အသုံးချမှုအလိုက် မတူညီသော ဒီဇိုင်းများနှင့် မောင်းနှင်မှုနည်းလမ်းများ ရှိမည်ဖြစ်သည်။ လည်ပတ်မော်တာများ၏အသုံးပြုမှုများအရ၊ အောက်ပါအခြေခံအမျိုးအစားများကိုပြုလုပ်ထားပြီး၊ ကျွန်ုပ်တို့သည် မော်တာများတွင် ကိုယ်စားလှယ်အများဆုံး၊ အသုံးအများဆုံးနှင့် အခြေခံမော်တာများ - ထိန်းချုပ်မော်တာများ၊ ပါဝါမော်တာများနှင့် အချက်ပြမော်တာများကို အဓိကမိတ်ဆက်ပေးပါသည်။
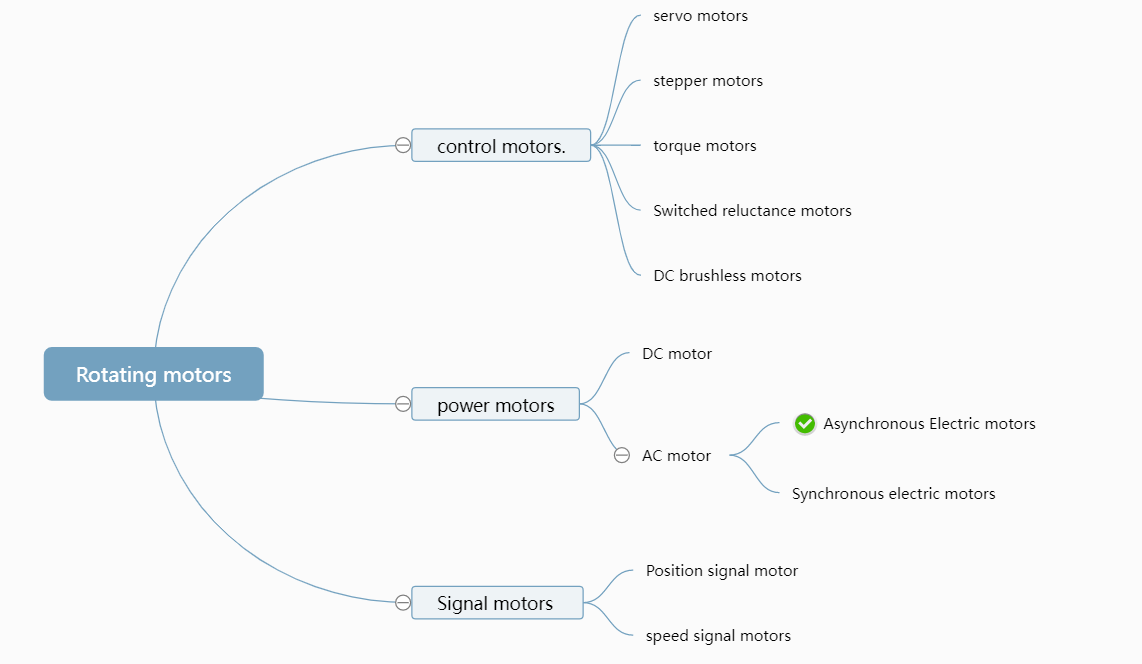
မော်တာများကို ထိန်းချုပ်ပါ။
Control motors are mainly used for precise speed and position control, and as "actuators" in control systems. They can be divided into servo motors, stepper motors, torque motors, switched reluctance motors, brushless DC motors and other categories.
Servo မော်တာများ
အစောဆုံး servo motor သည် ယေဘူယျ DC မော်တာဖြစ်ပြီး ထိန်းချုပ်မှု တိကျမှု မြင့်မားမှသာ ယေဘုယျအားဖြင့် DC မော်တာကို servo motor အဖြစ် အသုံးပြုပါသည်။ လက်ရှိ DC servo မော်တာသည် တည်ဆောက်ပုံအရ သေးငယ်သော ပါဝါ DC မော်တာဖြစ်ပြီး ၎င်း၏ စိတ်လှုပ်ရှားမှုသည် အများအားဖြင့် armature ထိန်းချုပ်မှုနှင့် သံလိုက်စက်ကွင်းထိန်းချုပ်မှုကို လက်ခံရရှိသော်လည်း များသောအားဖြင့် armature ထိန်းချုပ်မှုကို လက်ခံပါသည်။
Servo motor များကို ထိန်းချုပ်မှုစနစ်အမျိုးမျိုးတွင် အဓိကအားဖြင့် လှုပ်ရှားမှုထိန်းချုပ်မှုစနစ်များ အထူးသဖြင့် follow-me စနစ်များတွင် အသုံးများသည်။ ၎င်းသည် input voltage signal ကို motor shaft ပေါ်ရှိ စက်ပိုင်းဆိုင်ရာ output အဖြစ်သို့ ပြောင်းလဲနိုင်ပြီး control ရည်ရွယ်ချက်ကို အောင်မြင်ရန် ထိန်းချုပ်ထားသော element ကို ဆွဲယူနိုင်သည်။ ယေဘုယျအားဖြင့် servo motor သည် ထပ်လောင်းဗို့အားအချက်ပြမှုဖြင့် ထိန်းချုပ်ရန် မော်တာ၏အမြန်နှုန်းကို လိုအပ်သည်၊ ထပ်လောင်းဗို့အားအချက်ပြမှုပြောင်းလဲခြင်းဖြင့် အမြန်နှုန်းကို ဆက်တိုက်ပြောင်းလဲနိုင်သည်၊ torque ကို controller မှ လက်ရှိ output ဖြင့် ထိန်းချုပ်နိုင်ပြီး မော်တာ၊ လျင်မြန်စွာ ရောင်ပြန်ဟပ်သင့်သည်၊ အရွယ်အစားသေးငယ်ပြီး ထိန်းချုပ်မှုစွမ်းအား သေးငယ်သင့်သည်။
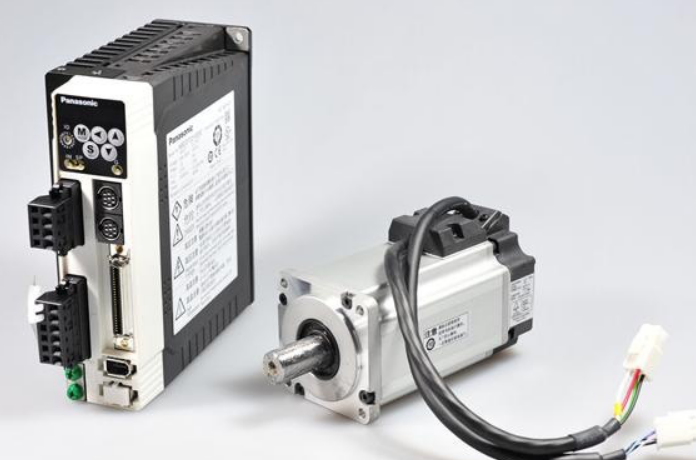

Stepper မော်တာ
Stepper မော်တာဟုခေါ်သော လျှပ်စစ်ပဲများကို အထောင့်ရွေ့ပြောင်းမှုအဖြစ်သို့ ပြောင်းလဲပေးသည့် actuator တစ်ခုဖြစ်သည်။ ဆိုလိုသည်မှာ၊ stepper driver သည် pulse signal ကိုလက်ခံရရှိသောအခါ၊ ၎င်းသည် set direction တွင် fixed angle ကိုလှည့်ရန် stepper motor ကိုမောင်းနှင်သည်။
ကျွန်ုပ်တို့သည် တိကျသောနေရာချထားခြင်း၏ရည်ရွယ်ချက်ကိုအောင်မြင်စေရန်အတွက် ပဲမျိုးစုံအရေအတွက်ကို ထိန်းချုပ်ခြင်းဖြင့် မော်တာ၏ angular displacement ကို ထိန်းချုပ်နိုင်သည်။
တစ်ချိန်တည်းမှာပင်၊ ကျွန်ုပ်တို့သည် အရှိန်ထိန်းညှိခြင်း၏ ရည်ရွယ်ချက်ကို အောင်မြင်စေရန်အတွက် သွေးခုန်နှုန်းကြိမ်နှုန်းကို ထိန်းချုပ်ခြင်းဖြင့် မော်တာလည်ပတ်မှု၏ အရှိန်နှင့် အရှိန်ကိုလည်း ထိန်းချုပ်နိုင်သည်။ လက်ရှိတွင်၊ အသုံးများသော stepper motor များတွင် reactive stepper motors (VR)၊ permanent magnet stepper motors (PM)၊ hybrid stepper motors (HB) နှင့် single-phase stepper motors တို့ ပါဝင်သည်။
Stepper မော်တာများနှင့် သာမန်မော်တာများကြား ခြားနားချက်မှာ ၎င်းတို့၏ Pulse-driver Form တွင် အဓိကအားဖြင့် တည်ရှိသောကြောင့် Stepper မော်တာများသည် ခေတ်မီဒစ်ဂျစ်တယ်ထိန်းချုပ်မှုနည်းပညာနှင့် ပေါင်းစပ်နိုင်ပြီး ရိုးရှင်းသောဖွဲ့စည်းပုံ၊ ယုံကြည်စိတ်ချရမှုမြင့်မားပြီး ကုန်ကျစရိတ်သက်သာသော ဝိသေသလက္ခဏာများရှိသည်။
သို့သော် ထိန်းချုပ်မှုတိကျမှု၊ မြန်နှုန်းပြောင်းလဲမှုအကွာအဝေးရှိ stepper မော်တာများသည် DC ဆာဗာမော်တာများ၏ ရိုးရာအပိတ်အပိတ်ထိန်းချုပ်မှုထက် နိမ့်ကျနေသောကြောင့် stepper motor များကို ထုတ်လုပ်မှုအလေ့အကျင့်များတွင် တွင်ကျယ်စွာအသုံးပြုကြပြီး အခြားသောတိကျမှုလိုအပ်ချက်များသည် နယ်ပယ်အသီးသီးတွင် အထူးမြင့်မားခြင်းမရှိပါ။ အထူးသဖြင့် CNC စက်ကိရိယာထုတ်လုပ်မှုနယ်ပယ်တွင်။
နှင့် stepper motor များသည် A/D ပြောင်းလဲခြင်းမလိုအပ်ပါ၊ ဒစ်ဂျစ်တယ်သွေးခုန်နှုန်းအချက်ပြမှုကို angular displacement အဖြစ်သို့တိုက်ရိုက်ပြောင်းလဲနိုင်သောကြောင့်၎င်းကိုအကောင်းဆုံးစံပြ CNC စက်ကိရိယာ actuators အဖြစ်သတ်မှတ်ထားသည်။
CNC စက်ကိရိယာများတွင် ၎င်းတို့၏ အသုံးချမှုအပြင်၊ အလိုအလျောက် အစာပေးကိရိယာများရှိ မော်တာများ၊ အထွေထွေသုံး ဖလော်ပီဒစ်ဒရိုက်များတွင် မော်တာများ၊ နှင့် ပရင်တာများနှင့် ကွက်ကွက်များကဲ့သို့သော အခြားစက်များတွင်လည်း အသုံးပြုနိုင်သည်။

ထို့အပြင်၊ stepper motor တွင်လည်းချို့ယွင်းချက်များစွာရှိသည်။ stepper motor ၏ no-load start frequency ကြောင့် stepper motor သည် နိမ့်သောအမြန်နှုန်းဖြင့် ပုံမှန်လည်ပတ်နိုင်သော်လည်း အချို့သောအမြန်နှုန်းထက် မြင့်ပါက မစတင်နိုင်ဘဲ စူးရှသော လေချွန်သံဖြင့် လိုက်ပါသွားပါသည်။ ခွဲခွဲဒရိုက်၏ တိကျမှု ကွဲပြားသော ထုတ်လုပ်သူများသည် များစွာကွဲပြားနိုင်သည်၊ ခွဲခွဲတိကျမှု ကြီးလေလေ ထိန်းချုပ်ရန် ပိုခက်ခဲလေဖြစ်သည်။ Stepper motor တွင် မြန်နှုန်းနိမ့် လည်ပတ်မှုတွင် ကြီးမားသောတုန်ခါမှုနှင့် ဆူညံမှုရှိသည်။
Torque မော်တာ
torque motor ဟုခေါ်သော ပြားချပ်ချပ် အမျိုးအစား Multi-pole အမြဲတမ်း သံလိုက် DC မော်တာ ဖြစ်သည်။
၎င်း၏ armature တွင် torque pulsation နှင့် speed pulsation ကိုလျှော့ချရန် ပိုမိုများပြားသော slots များ၊ commutation plates နှင့် series conductors များရှိသည်။ torque မော်တာ အမျိုးအစား နှစ်မျိုးရှိပြီး DC torque motor နှင့် AC torque motors များ ဖြစ်သည်။

၎င်းတို့တွင် DC torque motor တွင် self-induced reactance သေးငယ်သောကြောင့် တုံ့ပြန်မှု ကောင်းမွန်ပါသည်။ ၎င်း၏ output torque သည် rotor ၏ အမြန်နှုန်းနှင့် အနေအထားကို မှီတည်ပြီး input current နှင့် အချိုးကျပါသည်။ ၎င်းသည် ဂီယာလျော့ချခြင်းမရှိဘဲ ဝန်နှင့် တိုက်ရိုက်ချိတ်ဆက်ထားသော အမြန်နှုန်းနိမ့်ဖြင့် လည်ပတ်နိုင်ပြီး၊ ထို့ကြောင့် ၎င်းသည် ဝန်၏ရိုးရိုးပေါ်တွင် မြင့်မားသော torque to inertia အချိုးကို ထုတ်လုပ်နိုင်ပြီး လျှော့ချဂီယာများကို အသုံးပြုခြင်းကြောင့် စနစ်တကျ အမှားအယွင်းများကို ဖယ်ရှားပေးနိုင်သည်။
AC torque မော်တာများကို synchronous နှင့် asynchronous ဟူ၍ ပိုင်းခြားနိုင်ပြီး လက်ရှိအသုံးများသည့် ရှဉ့်လှောင်အိမ်မှ အမြန်နှုန်းနိမ့် နှင့် ကြီးမားသော torque တို့၏ ဝိသေသလက္ခဏာများ ရှိသည့် ရှဉ့်-လှောင်အိမ် မှ တပြိုင်နက် ရုန်းအား မော်တာ ဖြစ်ပါသည်။ ယေဘုယျအားဖြင့် AC torque motor များကို အထည်အလိပ်လုပ်ငန်းတွင် အသုံးပြုလေ့ရှိသည်။ ၎င်းတို့၏ လုပ်ဆောင်မှု နိယာမနှင့် ဖွဲ့စည်းပုံသည် single-phase asynchronous motors များနှင့် တူညီသော်လည်း Squirrel-cage rotor ၏ ခံနိုင်ရည် မြင့်မားမှုကြောင့် ၎င်းတို့၏ စက်ပိုင်းဆိုင်ရာ လက္ခဏာများသည် ပိုမိုပျော့ပျောင်းပါသည်။
တွန့်ဆုတ်နေသော မော်တာကို ပြောင်းခြင်း။
Switched တုံ့ဆိုင်းနေသော မော်တာသည် မြန်နှုန်းထိန်းမော်တာ အမျိုးအစားအသစ်ဖြစ်ပြီး အလွန်ရိုးရှင်းပြီး ကြံ့ခိုင်ဖွဲ့စည်းပုံ၊ ကုန်ကျစရိတ် သက်သာသော၊ အလွန်ကောင်းမွန်သော အမြန်နှုန်းထိန်းချုပ်မှု စွမ်းဆောင်ရည်၊ သမားရိုးကျ ထိန်းချုပ်မော်တာ၏ ပြင်းထန်သော ပြိုင်ဘက်ဖြစ်ပြီး စျေးကွက်အလားအလာ အားကောင်းသည်။
သို့သော်၊ လက်တွေ့စျေးကွက်အပလီကေးရှင်းနှင့်လိုက်လျောညီထွေဖြစ်အောင်လုပ်ဆောင်ရန်အချိန်အနည်းငယ်လိုအပ်သော torque pulsation၊ operating noise နှင့် vibration ကဲ့သို့သောပြဿနာများရှိပါသည်။
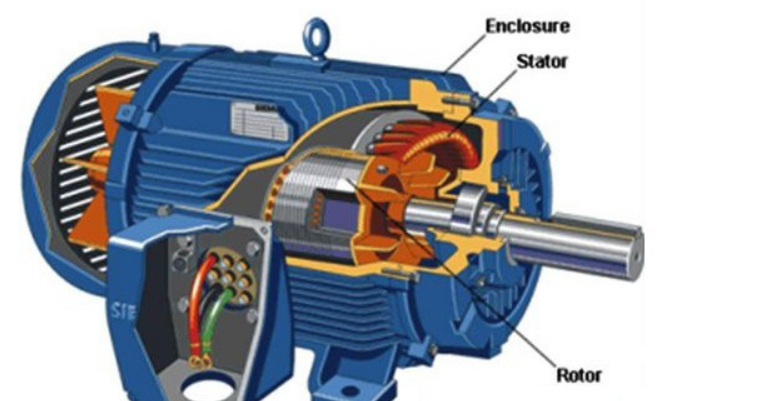
Brushless DC မော်တာ
Brushless DC motor (BLDCM) is developed on the basis of brushed DC motor, but its drive current is uncompromisingly AC. Brushless DC motors can be further divided into brushless rate motors and brushless torque motors. Generally, brushless motors have two types of drive currents, one is a trapezoidal wave (usually a "square wave") and the other is a sine wave. Sometimes the former is called a brushless DC motor and the latter is called an AC servo motor, which is also a kind of AC servo motor to be exact.
Brushless DC motors usually have a "slender" structure in order to reduce rotational inertia. Brushless DC motors are much smaller in weight and volume than brushed DC motors, and the corresponding rotational inertia can be reduced by about 40%-50%. Due to the processing problems of permanent magnet materials, the capacity of brushless DC motors is generally below 100kW.
ဤမော်တာ၏ စက်ပိုင်းဆိုင်ရာ ဝိသေသလက္ခဏာများနှင့် စည်းမျဥ်းစည်းကမ်းဝိသေသများသည် ကောင်းမွန်သော linearity၊ ကျယ်ပြန့်သောအမြန်နှုန်း၊ ကြာရှည်စွာ၊ ပြုပြင်ထိန်းသိမ်းရလွယ်ကူပြီး ဆူညံသံနည်းပါးကာ၊ စုတ်တံကြောင့်ဖြစ်ရသည့် ပြဿနာများ ဆက်တိုက်မရှိသောကြောင့် ဤမော်တာသည် ထိန်းချုပ်မှုစနစ်များတွင် အသုံးပြုရန်အတွက် အလားအလာကောင်းများရှိပါသည်။

Brushless DC motors are usually of "slender" construction to reduce the inertia.
Brushless DC မော်တာများသည် brushed DC မော်တာများထက် အလေးချိန်နှင့် ထုထည်ပိုမိုသေးငယ်ပြီး သက်ဆိုင်ရာ rotational inertia ကို 40%-50% ခန့် လျှော့ချနိုင်သည်။ အမြဲတမ်းသံလိုက်ပစ္စည်းများ၏လုပ်ဆောင်မှုပြဿနာများကြောင့်၊ brushless DC မော်တာများ၏စွမ်းရည်သည် ယေဘုယျအားဖြင့် 100kW အောက်တွင်ရှိသည်။
ဤမော်တာ၏ စက်ပိုင်းဆိုင်ရာ ဝိသေသလက္ခဏာများနှင့် စည်းမျဥ်းစည်းကမ်းဝိသေသများသည် ကောင်းမွန်သော linearity၊ ကျယ်ပြန့်သောအမြန်နှုန်း၊ ကြာရှည်စွာ၊ ပြုပြင်ထိန်းသိမ်းရလွယ်ကူပြီး ဆူညံသံနည်းပါးကာ၊ စုတ်တံကြောင့်ဖြစ်ရသည့် ပြဿနာများ ဆက်တိုက်မရှိသောကြောင့် ဤမော်တာသည် ထိန်းချုပ်မှုစနစ်များတွင် အသုံးပြုရန်အတွက် အလားအလာကောင်းများရှိပါသည်။
ပါဝါမော်တာ
ပါဝါမော်တာအား DC မော်တာနှင့် AC မော်တာဟူ၍ ပိုင်းခြားထားပြီး AC မော်တာကို အဓိကအားဖြင့် synchronous motor နှင့် asynchronous motor ဟူ၍ ခွဲခြားထားသည်။
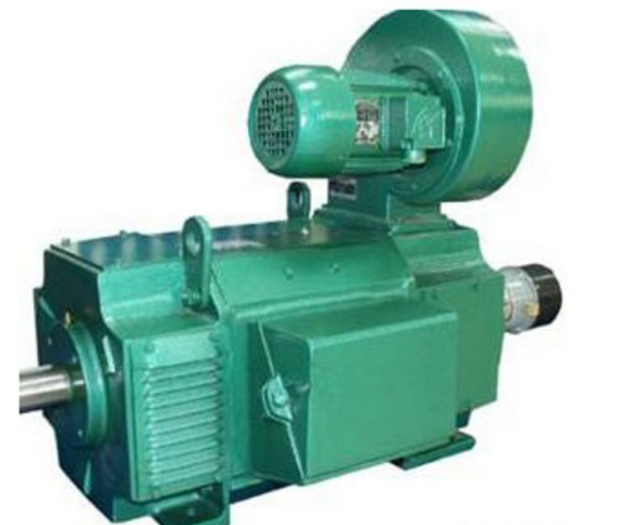
DC မော်တာ
DC motor သည် 19 ရာစုနှောင်းပိုင်းလောက်က အစောဆုံးသော မော်တာဖြစ်ပြီး အကြမ်းဖျင်းအားဖြင့် ကွန်မြူတာတာနှင့် ကွန်မြူတာတာမပါသော အမျိုးအစားနှစ်မျိုး ခွဲခြားနိုင်သည်။
DC မော်တာတွင် ပိုမိုကောင်းမွန်သော ထိန်းချုပ်မှုလက္ခဏာများ ရှိသော်လည်း ဖွဲ့စည်းပုံအရ၊ ဈေးနှုန်းနှင့် ပြုပြင်ထိန်းသိမ်းမှုမှာ AC မော်တာကဲ့သို့ ကောင်းမွန်ခြင်းမရှိပေ။
AC motor ၏ speed control ပြဿနာကို ကောင်းစွာမဖြေရှင်းနိုင်သောကြောင့် DC motor တွင် speed control performance ကောင်းမွန်ပြီး၊ စတင်ရန်လွယ်ကူသည်၊ load start လုပ်နိုင်ခြင်း၊
အထူးသဖြင့် ဆီလီကွန်ထိန်းချုပ်ထားသော DC ပါဝါထောက်ပံ့မှု ပေါ်ပေါက်လာပြီးနောက် DC မော်တာ၏ အသုံးချမှုသည် အလွန်ကျယ်ပြန့်ဆဲဖြစ်သည်။
လျှောက်လွှာအခြေအနေ- ဘဝတွင်၊ ပန်ကာများ၊ သင်တုန်းဓားများ၊ ဟိုတယ်များတွင် အလိုအလျောက်တံခါးများ၊ အလိုအလျောက်တံခါးသော့များ၊ အလိုအလျောက် ကန့်လန့်ကာများ စသည်တို့ကဲ့သို့သော လျှပ်စစ်ထုတ်ကုန်များ၏ မရေမတွက်နိုင်သော အပလီကေးရှင်းများ ရှိသည်၊ အားလုံးသည် DC မော်တာများကို အသုံးပြုကြသည်။
DC မော်တာများကို မီးရထားစက်ခေါင်းများအတွက် DC traction motors၊ မြေအောက်ရထားစက်ခေါင်းများအတွက် DC traction motors၊ စက်ခေါင်းများအတွက် DC အရန်မော်တာများ၊ သတ္တုတွင်းစက်ခေါင်းများအတွက် DC traction motors၊ သင်္ဘောများအတွက် DC မော်တာစသည်ဖြင့် DC မော်တာများကဲ့သို့ စက်ခေါင်းများတွင် တွင်ကျယ်စွာအသုံးပြုပါသည်။
၎င်းတို့ကို လေယာဉ်၊ တင့်ကားများ၊ ရေဒါနှင့် အခြားလက်နက်များနှင့် ကိရိယာများတွင်လည်း တွင်ကျယ်စွာ အသုံးပြုကြသည်။ ပုံတွင် Z4 စီးရီး DC မော်တာကို ပြသထားသည်။

AC မော်တာ
Synchronous မော်တာ
synchronous motor ဟုခေါ်သော လျှပ်စစ်မော်တာသည် လျှပ်စီးကြောင်းဖြင့် မောင်းနှင်သော လျှပ်စစ်မော်တာဖြစ်ပြီး၊ ရဟတ်နှင့် stator လည်ပတ်နေသော သံလိုက်စက်ကွင်းသည် တပြိုင်တည်းလည်ပတ်နေသည်။
The stator of synchronous motor is exactly the same as that of asynchronous motor, but there are two types of rotor: "convex pole" and "hidden pole".
ခုံးရဟတ် synchronous မော်တာသည် ရိုးရှင်းပြီး ထုတ်လုပ်ရန် လွယ်ကူသော်လည်း စက်ပိုင်းဆိုင်ရာ ကြံ့ခိုင်မှု နည်းပါးပြီး မြန်နှုန်းနိမ့် လည်ပတ်မှုအတွက် သင့်လျော်သည်။
hidden pole synchronous motor သည် ရှုပ်ထွေးသော ထုတ်လုပ်မှု လုပ်ငန်းစဉ်တွင် ပါဝင်သော်လည်း စက်ပိုင်းဆိုင်ရာ စွမ်းအား မြင့်မားပြီး မြန်နှုန်းမြင့် လည်ပတ်မှုအတွက် သင့်လျော်ပါသည်။
The working characteristic of synchronous motor is the same as all motors, which is "reversible", that is, it can run in generator mode and motor mode.
လျှောက်လွှာအခြေအနေ- ချိန်ကိုက်မော်တာများကို လေမှုတ်စက်များ၊ ပန့်များ၊ ဘောကြိတ်စက်များ၊ ကွန်ပရက်ဆာများ၊ သံမဏိလှိမ့်စက်များ၊ အသေးစားနှင့် အသေးစားတူရိယာများနှင့် စက်ကိရိယာများ သို့မဟုတ် ထိန်းချုပ်ဒြပ်စင်များအဖြစ်၊ သုံးဆင့်ထပ်တူသောမော်တာများသည် ပင်မကိုယ်ထည်ကဲ့သို့သော ကြီးမားသောစက်များတွင် အဓိကအသုံးပြုကြသည်။ .
ထို့အပြင်၊ ၎င်းအား grid သို့ inductive သို့မဟုတ် capacitive reactive power ပေးပို့ရန် regulator အဖြစ်လည်းအသုံးပြုနိုင်ပါသည်။

Asynchronous မော်တာ
Asynchronous motor သည် လျှပ်စစ်သံလိုက် torque ကိုထုတ်လုပ်ရန်နှင့် စွမ်းအင်ပြောင်းလဲခြင်းကို သိရှိနားလည်ရန် လေထုကွာဟချက်အား လည်ပတ်နေသော သံလိုက်စက်ကွင်းနှင့် rotor winding induction current တို့အပေါ် အခြေခံ၍ AC motor အမျိုးအစားဖြစ်သည်။
Asynchronous motor သည် ယေဘူယျအားဖြင့် သတ်မှတ်ချက်များ ကျယ်ပြန့်သော ထုတ်ကုန်စီးရီးဖြစ်ပြီး ၎င်းသည် မော်တာအားလုံးတွင် အသုံးအများဆုံးနှင့် အလိုအပ်ဆုံးဖြစ်သည်။
လက်ရှိတွင် ဓာတ်အားပို့လွှတ်မှုတွင် စက်ယန္တရားများ၏ 90% ခန့်သည် AC asynchronous motor ကိုအသုံးပြုထားသောကြောင့် ၎င်း၏လျှပ်စစ်သုံးစွဲမှုသည် စုစုပေါင်းလျှပ်စစ်ဝန်၏ထက်ဝက်ကျော်ရှိသည်။
ဗီဒီယိုကို စစ်ဆေးပါ။ Asynchronous မော်တာ၏ထုတ်လုပ်သူ
Asynchronous မော်တာသည် ရိုးရှင်းသောဖွဲ့စည်းပုံ၊ လွယ်ကူစွာထုတ်လုပ်ခြင်း၊ အသုံးပြုခြင်းနှင့် ထိန်းသိမ်းခြင်း၊ ယုံကြည်စိတ်ချရသောလည်ပတ်မှုအပြင် သေးငယ်သောထုထည်နှင့် ကုန်ကျစရိတ်သက်သာခြင်း၏ အားသာချက်များရှိသည်။
ထို့အပြင်၊ asynchronous motor သည် မြင့်မားသော လည်ပတ်မှု စွမ်းဆောင်ရည်နှင့် ကောင်းမွန်သော အလုပ်သွင်ပြင်လက္ခဏာများ ဖြစ်သည့် ဝန်အားမရှိချိန်မှ ဝန်အားအပြည့် အကွာအဝေးအထိ အဆက်မပြတ် အမြန်နှုန်းဖြင့် လည်ပတ်နိုင်ပြီး စက်မှုနှင့် စိုက်ပျိုးရေး ထုတ်လုပ်မှု စက်ပစ္စည်းအများစု၏ ဂီယာလိုအပ်ချက်များကို ဖြည့်ဆည်းပေးနိုင်ပါသည်။
Asynchronous မော်တာများကို မောင်းနှင်သည့် စက်ကိရိယာများ၊ ပန့်များ၊ လေမှုတ်ကိရိယာများ၊ ကွန်ပရက်ဆာများ၊ ရုတ်သိမ်းခြင်းနှင့် အကွေ့အကောက်များသော စက်ကိရိယာများ၊ သတ္တုတွင်းစက်ပစ္စည်းများ၊ အပေါ့စားစက်မှုလုပ်ငန်းသုံး စက်များ၊ စိုက်ပျိုးရေးနှင့် ဘေးထွက်လုပ်ငန်းသုံး စက်များနှင့် စက်မှုနှင့် စိုက်ပျိုးရေးဆိုင်ရာ ထုတ်လုပ်မှု စက်အများစုအပြင် အိမ်သုံးအသုံးအဆောင်များနှင့် ဆေးဘက်ဆိုင်ရာ ကိရိယာများတွင် ကျယ်ကျယ်ပြန့်ပြန့် အသုံးပြုကြသည်။
အသုံးချမှုအခြေအနေ- ပိုမိုအသုံးများသော အပျက်သဘောဆောင်သော မော်တာများသည် single-phase asynchronous motors နှင့် three-phase asynchronous motors များဖြစ်ပြီး ၎င်းတို့ထဲမှ three-phase asynchronous motor သည် asynchronous motor ၏ အဓိကကိုယ်ထည်ဖြစ်ပြီး၊ three-phase asynchronous motor အမျိုးမျိုးကို မောင်းနှင်နိုင်သည်။ ကွန်ပရက်ဆာများ၊ ပန့်များ၊ ကြိတ်စက်များ၊ ဖြတ်တောက်သည့်စက်ကိရိယာများ၊ သယ်ယူပို့ဆောင်ရေးစက်များနှင့် အခြားစက်ကိရိယာများ၊ သတ္တုတွင်း၊ စက်ပစ္စည်း၊ သတ္တုဗေဒ၊ ရေနံ၊ ဓာတုဗေဒစက်မှုလုပ်ငန်း၊ ဓာတ်အားပေးစက်ရုံများနှင့် အခြားစက်မှုလုပ်ငန်းနှင့် သတ္တုတွင်းလုပ်ငန်းများတွင် အဓိကအသုံးပြုသည့် မော်တာအဖြစ်၊ သတ္တုတွင်း၊ စက်ယန္တရား၊ သတ္တုဗေဒ၊ ရေနံ၊ ဓာတုစက်မှုလုပ်ငန်း၊ ဓာတ်အားပေးစက်ရုံနှင့် အခြားစက်မှုလုပ်ငန်းနှင့် သတ္တုတွင်းလုပ်ငန်းများတွင် အသုံးပြုသည်။
Single-phase asynchronous motor များကို ယေဘုယျအားဖြင့် သုံးဆင့်ပါဝါထောက်ပံ့မှု အဆင်မပြေသည့်နေရာများတွင် အများအားဖြင့် လျှပ်စစ်ပန်ကာများ၊ ရေခဲသေတ္တာများ၊ လေအေးပေးစက်များ၊ ဖုန်စုပ်စက်များကဲ့သို့သော အိမ်သုံးပစ္စည်းများတွင် ပိုမိုအသုံးပြုသည့် အသေးစားနှင့် အသေးစား စွမ်းရည်ရှိသော မော်တာများကို ယေဘုယျအားဖြင့် အသုံးပြုကြသည်။

အချက်ပြမော်တာ
အနေအထားအချက်ပြမော်တာ
လက်ရှိတွင်၊ အများဆုံးကိုယ်စားပြုအနေအထားအချက်ပြမော်တာများ- ဖြေရှင်းသူ၊ induction synchronizer နှင့် self-adjusting angle စက်။
(၁) Rotary Transformer ၊
Rotary transformer သည် synchronous decomposer ဟုခေါ်သော လျှပ်စစ်သံလိုက်အာရုံခံကိရိယာတစ်ခုဖြစ်သည်။ ၎င်းသည် ထောင့်တိုင်းတိုင်းတာရန်အတွက် အသေးစား AC မော်တာဖြစ်ပြီး၊ လှည့်နေသောအရာဝတ္ထု၏ angular displacement နှင့် angular velocity ကိုတိုင်းတာရန်အသုံးပြုကာ stator နှင့် rotor တစ်ခုပါဝင်သည်။ stator winding ကို excitation voltage ကိုလက်ခံရရှိရန် transformer ၏ အဓိကအခြမ်းအဖြစ်အသုံးပြုပြီး excitation frequency ကို များသောအားဖြင့် 400, 3000 နှင့် 5000 HZ စသည်တို့ဖြစ်သည်။ excitation voltage ကိုရရှိရန် rotor winding ကို transformer ၏ ဒုတိယအခြမ်းအဖြစ် အသုံးပြုပါသည်။ . ရဟတ်အကွေ့အကောက်များကို လျှပ်စစ်သံလိုက်အချိတ်အဆက်မှတဆင့် လျှပ်စီးကြောင်းဗို့အားရရှိရန် ထရန်စဖော်မာ၏ ဒုတိယအခြမ်းအဖြစ် အသုံးပြုသည်။
အပလီကေးရှင်းအခြေအနေ- ဖြေရှင်းပေးသူသည် အထူးသဖြင့် မြင့်မားသောအပူချိန်၊ အအေးမိ၊ စိုထိုင်းဆ၊ မြန်နှုန်းမြင့်၊ တုန်ခါမှုမြင့်မားခြင်းနှင့် rotary ကုဒ်ပြောင်းကိရိယာကို အသုံးပြု၍ မရနိုင်သော အခြားအချိန်များတွင် rotary transformer ဖြေရှင်းသည့်အချိန်တိုင်းအတွက် သင့်လျော်သော တိကျသောထောင့်၊ အနေအထားနှင့် အမြန်နှုန်းသိရှိနိုင်သောကိရိယာဖြစ်သည်။ ကောင်းစွာအလုပ်လုပ်။ rotary transformer ၏ အထက်ဖော်ပြပါ လက္ခဏာများကြောင့်၊ ၎င်းသည် photoelectric encoder ကို အပြီးအပြတ် အစားထိုးနိုင်ပြီး servo ထိန်းချုပ်မှုစနစ်၊ စက်ရုပ်စနစ်၊ စက်ကိရိယာများ၊ မော်တော်ကား၊ လျှပ်စစ်စွမ်းအင်၊ သတ္တုဗေဒ၊ အထည်အလိပ်စသည့် နယ်ပယ်များတွင် ထောင့်နှင့် အနေအထား ထောက်လှမ်းမှုစနစ်တွင် တွင်ကျယ်စွာ အသုံးပြုပါသည်။ ပုံနှိပ်ခြင်း၊ အာကာသယာဉ်၊ သင်္ဘော၊ လက်နက်၊ အီလက်ထရွန်နစ်ပစ္စည်း၊ သတ္တုဗေဒ၊ သတ္တုတွင်း၊ ရေနံမြေ၊ ရေထိန်းသိမ်းမှု၊ ဓာတုစက်မှုလုပ်ငန်း၊ အပေါ့စားစက်မှုလုပ်ငန်း၊ ဆောက်လုပ်ရေး၊ စသည်ဖြင့်၊ ၎င်းကို coordinate transformation၊ trigonometric operation နှင့် angle data transmission တို့တွင်လည်း အသုံးပြုနိုင်သည်။ ထောင့်-ဒစ်ဂျစ်တယ်ပြောင်းလဲခြင်းကိရိယာတွင်အဆင့်အဆင့်ပြောင်းစက်။
Induction synchronizer
Induction synchronizer သည် မျဥ်းအကွေ့အကောက်နှစ်ခု၏ အပြန်အလှန် inductance သည် အနေအထားနှင့် ကွဲပြားပြီး linear သို့မဟုတ် angular displacement ကို တိုင်းတာရန်အတွက် အသုံးပြုခြင်းဖြင့် ဖွဲ့စည်းထားသည်။ ၎င်းတို့တွင် linear displacement တိုင်းတာခြင်းကို linear induction synchronizer (သို့မဟုတ် long induction synchronizer) ဟုခေါ်ပြီး angular displacement တိုင်းတာခြင်းကို side induction synchronizer (သို့မဟုတ် rotary induction synchronizer) ဟုခေါ်သည်။ Synchronizers များသည် စုစည်းမှုတိုင်းတာခြင်း၏ မြင့်မားသောတိကျမှုနှင့် ပြတ်သားမှုတို့၊ ပြင်းထန်သောဝင်ရောက်စွက်ဖက်မှုဆန့်ကျင်နိုင်စွမ်း၊ ပတ်ဝန်းကျင်လွှမ်းမိုးမှုနည်းသော၊ တာရှည်ဝန်ဆောင်မှုသက်တမ်း၊ ရိုးရှင်းသောပြုပြင်ထိန်းသိမ်းမှု၊ တိုင်းတာမှုအလျားအမျိုးမျိုးသို့ ပိုင်းခြားနိုင်ပြီး ယူနစ်တိကျမှု၊ ကောင်းမွန်စွာလုပ်ဆောင်နိုင်မှု၊ ကုန်ကျစရိတ်သက်သာမှု၊ ကော်ပီနှင့် အသုတ်ထုတ်လုပ်ရန် လွယ်ကူသည်။ ထို့ကြောင့်၊ synchronizers များကို display သို့မဟုတ် control devices များပေးဆောင်ရန် ဒစ်ဂျစ်တယ်နေရာချထားမှုအဖြစ် ကြီးမားသော စက်ကိရိယာများနှင့် အလတ်စားစက်များတွင် ကျယ်ကျယ်ပြန့်ပြန့်အသုံးပြုကြသည်။
လျှောက်လွှာအခြေအနေ- Induction synchronizers များသည် ၎င်းတို့နှင့်သက်ဆိုင်သည့် linear displacement၊ angular displacement နှင့် physical quantity များဖြစ်သည့် rotational speed, vibration, etc. Linear induction synchronizer ကို ကြီးမားသောတိကျသောစက်ကိရိယာများ၊ coordinate milling machines နှင့် အခြားသော CNC စက်များတွင် အသုံးပြုလေ့ရှိပါသည်။ ကိရိယာများ တည်နေရာထိန်းချုပ်မှုနှင့် ဒစ်ဂျစ်တယ်ပြသမှု၊ စက်ဝိုင်းပုံ induction synchronizer ကို အင်တာနာပုံသေခြေရာခံခြင်း၊ တိကျသေချာသောလမ်းညွှန်ချက်၊ တိကျသောစက်ကိရိယာများ သို့မဟုတ် တိုင်းတာခြင်းတူရိယာများနှင့် စက်ပစ္စည်းအညွှန်းကိန်းကိရိယာများ စသည်တို့ကိုရောက်ရှိရန် လိုအပ်သောနေရာတွင် အသုံးပြုလေ့ရှိသည်။
ကိုယ်တိုင်ချိန်ညှိခြင်းထောင့်စက်
Self-aligning angle machine သည် AC voltage သို့ angle ၏ self-aligning character များကို အသုံးပြုခြင်း သို့မဟုတ် AC voltage မှ induction micro-motor ၏ angle သို့ servo system တွင် displacement sensor အဖြစ် အသုံးပြုပါသည်။ အကွာအဝေးအတွင်း ထောင့်အချက်ပြမှုများကို ထုတ်လွှင့်ခြင်း၊ အသွင်ပြောင်း၊ လက်ခံခြင်းနှင့် ညွှန်ပြရန်အတွက် Self-aligning စက်များကို အသုံးပြုနိုင်သည်။ မော်တာနှစ်လုံး သို့မဟုတ် ထို့ထက်မကသော မော်တာနှစ်ခုကို စက်ဖြင့်ချိတ်ဆက်ထားခြင်းမဟုတ်သော လည်ပတ်မှုပုဆိန်နှစ်ခု သို့မဟုတ် ထို့ထက်ပိုသော လည်ပတ်မှုပုဆိန်များသည် တူညီသောထောင့်ပြောင်းလဲမှုကို အလိုအလျောက်ထိန်းထားနိုင်စေရန် သို့မဟုတ် တစ်ပြိုင်နက်တည်း လှည့်ပတ်ကာ မော်တာ၏ ဤပိုင်ဆိုင်မှုကို self-integrating step characteristic ဟုခေါ်သည်။ ဆာဗိုစနစ်တွင်၊ ထုတ်လုပ်သည့်ဘက်ခြမ်းတွင်အသုံးပြုသည့် အလိုအလျောက်ချိန်ညှိသည့်စက်ကို transmitter ဟုခေါ်ပြီး လက်ခံသည့်ဘက်တွင်အသုံးပြုသည့် စိတ်ကြိုက်ချိန်ညှိစက်ကို လက်ခံသူဟုခေါ်သည်။
အသုံးချမှုအခြေအနေ- Self-aligning angle စက်ကို သတ္တုဗေဒ၊ လမ်းကြောင်းပြခြင်းနှင့် အခြားသော အနေအထားနှင့် တိမ်းညွှတ်မှု ထပ်တူပြုမှု ညွှန်ပြစနစ်နှင့် အမြောက်များ၊ ရေဒါနှင့် အခြားသော ဆာဗာစနစ်များတွင် တွင်ကျယ်စွာ အသုံးပြုပါသည်။
ဤသည်မှာ မော်တာအမျိုးအစားနှင့် ပတ်သက်သော အချက်အလက်အချို့၏ အကျဉ်းချုပ်ဖြစ်သည်၊ ချို့ယွင်းချက် သို့မဟုတ် သင့်လျော်သောနေရာရှိပါက မှတ်ချက်ချန်ထားခဲ့ရန် ကြိုဆိုပါသည်။ ကျေးဇူးတင်ပါသည်!
ကျွန်ုပ်တို့သည် တရုတ်နိုင်ငံရှိ လျှပ်စစ်မော်တာများ၏ ပရော်ဖက်ရှင်နယ် ထုတ်လုပ်သူဖြစ်သည်။

တောင်းဆိုစရာရှိရင် ကျေးဇူးပြု၍ ကျွန်ုပ်တို့ကို အသိပေးပါ။
ဆက်စပ်ပို့စ်များ-







၂ တုံ့ပြန်မှုများ
ဟေး၊ မင်းရဲ့ဆောင်းပါးကို ငါဖတ်ပြီး မင်းရဲ့အချက်အလက်တွေက အရမ်းအံ့သြစရာကောင်းပြီး ငါ့အတွက် အများကြီးအထောက်အကူဖြစ်စေတယ်။ ဆက်လက်ပြီး ကျေးဇူးအများကြီးတင်ပါတယ်။ 🙂နောက်ထပ်အချက်အလက်တွေကို မှာနိုင်ပါတယ်။ https://tsca.com.ph/
သင်၏ကြင်နာသောမှတ်ချက်များအတွက်ကျေးဇူးတင်ပါသည်။